Cannabis cultivators consider several factors to achieve a high yield and THC levels out of their harvests. Things like the amount of water used, nutrients added, and the amount of sunlight provided must be calculated and perfected to ensure a consistent, usable product.
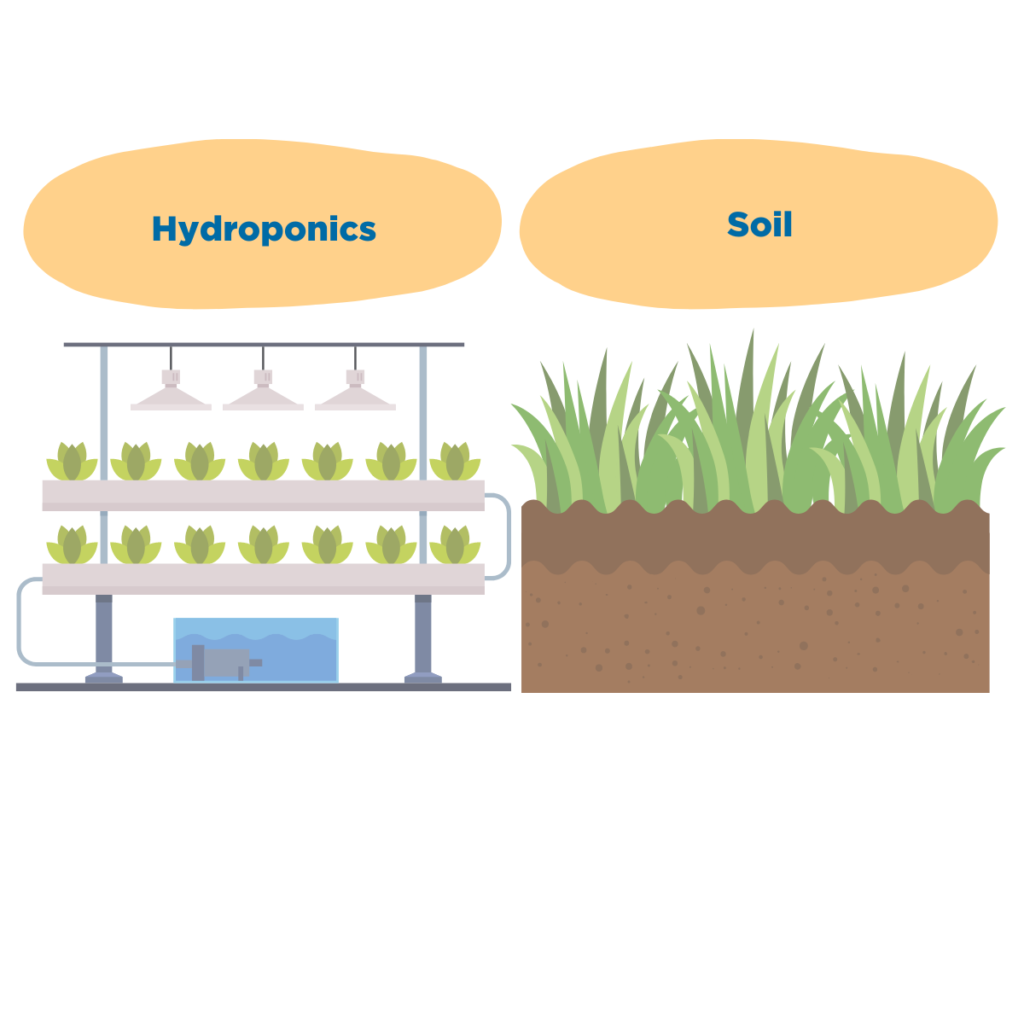
There are two main strategies most cultivators use to grow cannabis: soil or hydroponic growing. Hydroponic growing utilizes water instead of soil. When using a hydroponic growing technique, another grow medium is used to keep the plant upright, and the plants’ roots are exposed directly to water. Let’s break down the differences and similarities between growing hydroponically vs. in soil.
Growing cannabis in soil is flexible and can be done indoors or outdoors, whereas hydroponic structures must be inside. Growing outside is ideal when a cultivator is looking to reduce their overhead and can take advantage of the natural soil and light to grow their plants. Indoor structures give cultivators more control but at a higher expense. Hydroponic growing indoors is also more expensive at the beginning compared to utilizing soil indoors because of the equipment size and cost. However, in the long run, hydroponic cultivation sites become automated, and labor costs can be less than a soil grow.
When utilizing soil as the primary growing medium, the water will often seep down past the roots, and there is a lot of water waste. With hydroponic growing, the exact right amount of water is being used, and no water is wasted. There are many variations of hydroponic growing, and how the water reaches the roots vary substantially. A few common hydroponic systems are deep water culture, top-fed deep-water culture, nutrient film technique, ebb & flow, aquaponics, aeroponics, and the drip system. Cultivators using hydroponics tend to have a well-established process, ensuring consistency in both yield and flavor.